A garden room cost breaks down from foundation to fixtures with real-number detail you can trust. Start with site assessment, permits, and a foundation plan, then budget for groundworks and drainage. Framing, insulation, and shell depend on room size and materials, followed by roofing and weatherproofing. Interiors cover fixtures, utilities, and finishes, plus permits and contingencies. Expect 5–15% hidden fees and maintenance. If you keep exploring, you’ll uncover more precise cost drivers and example budgets.
Planning and Permits Overview
Planning and permits are the foundation of a garden room project. You’ll assess local planning rules, zoning constraints, and any owner-occupier limits that affect size, orientation, and usage.
Start with a concise site survey: dimensions, setbacks, and adjacency to property lines. You’ll identify permit pathways, timelines, and required documentation, including scaled plans, elevation drawings, and material lists.
Build a permit calendar with milestone dates, submission windows, and expected review durations. You’ll quantify compliance costs, application fees, and potential waivers, keeping contingencies tight at 5–15% of total permit expenses.
You’ll verify utility access, drainage requirements, and fire-safety standards early to avoid redesigns. Finally, you’ll track changes through a rigorous version-control log, ensuring traceability for inspectors and future maintenance.
Foundation and Groundwork Costs
With permits and site surveys in place, you can move to the foundations and groundwork where cost accuracy starts. In this section, you’ll see the main drivers: soil conditions, trenching depth, concrete type, reinforcement, and site access.
Expect variances from soil tests, moisture, and frost considerations that influence piling or slab choices. A typical slab-on-grade, including excavation, formwork, rebar, vapor barrier, and concrete, lands in a narrow range per square meter, plus setup fees.
If your site needs drainage, under-slab drains and compacted fill add measurable costs. Utility trenching, connection meters, and temporary access roads can shift budgets by several hundred to thousands, depending on length and obstacles.
Plan for a contingency of 5–15% to cover unexpected subsurface conditions.
Framing, Insulation, and Shell
Framing, insulation, and the shell set the building envelope and thermal performance, so accurate costs hinge on structural design choices, material specs, and airtightness targets.
You’ll quantify framing in square meters and lumber grade, then apply connector counts and fastener types to yield installed cost per unit.
Insulation costs rely on R-value targets, with boundary conditions driving cavity fill vs. continuous insulation, vapor retarders, and installed thickness.
Shell expenses include sheathing, air barriers, and finishing materials, plus seals for joints and penetrations.
Labor hours track complexity, overlaps with electrical and plumbing, and crane or lift needs for larger panels.
Material waste allowances, delivery windows, and weather contingencies affect fluctuations.
Deliverables: a bill of quantities, unit prices, and a risk-adjusted estimate with confidence intervals.
Roofing and Weatherproofing
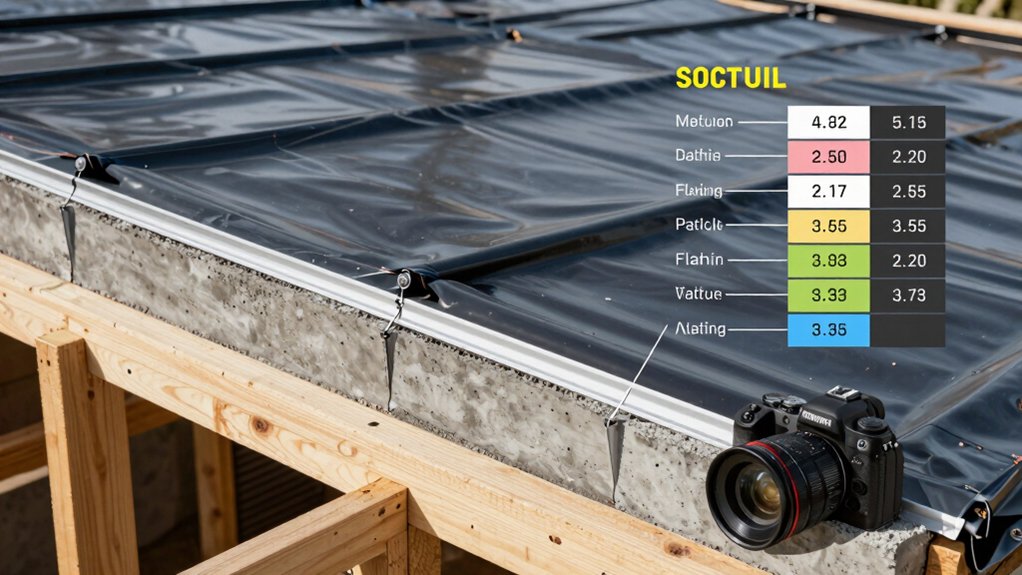

Roofing and weatherproofing establish the roof envelope, drive moisture control, and influence energy performance. You’ll quantify material choices, installation details, and detailing for penetrations to produce a transparent installed cost.
You measure roof types (mono-pitch, dual-slope, or flat), specify substrate, underlayment, and membrane options, and list thicknesses, R-values, and wind uplift ratings. You itemize fasteners, flashing, venting, and edge trim with unit costs and waste factors.
You document roof slope calculations, drainage strategy, and overhangs to project material and labor hours.
Weatherproofing follows with vapor retarders, sealants, and flashing at joints and penetrations, including seals around doors and utilities.
You forecast labor rates, equipment needs, inspection milestones, and contingencies, ensuring the total reflects pace, climate, and design tolerance.
Interiors, Fixtures, and Utilities
When planning interiors, fixtures, and utilities, you’ll weigh finishes and details, fittings, and installations against durability, maintenance, and upfront costs.
We’ll quantify material choices, labor hours, and energy efficiency to compare options and forecast total project spend.
This data-driven approach guides decisions on trims, fixtures, and wiring layouts to balance aesthetics with functional requirements.
Finishes and Details
Finishes and details cover the interior look and usability of the garden room, from wall finishes and flooring to lighting, outlets, and plumbing fixtures. You’ll quantify material choices by square footage, weight, and durability, avoiding over-spec.
Walls typically range from basic plaster to tongue-and-groove, with finishes priced per square meter and installed costs per wall area.
Flooring choices hinge on traffic, moisture exposure, and subfloor compatibility, tracked in price per square meter and underlayment requirements.
Lighting plans should specify lumens, color temperature, and electrical load, with fixture counts mapped to circuits and breaker ratings.
Outlet provision follows code, documented as receptacle density per room and higher-demand locations.
Plumbing fixtures, where applicable, are scoped for supply lines, waste routing, and access panels, with install hours and warranty terms recorded.
Fixtures and Fittings
Fixtures and fittings cover the interiors, utilities, and built-in components that determine daily usability, reliability, and efficiency. In this section, you’ll see quantified costs for cabinets, countertops, sinks, faucets, lighting, switches, outlets, and HVAC-compatible fixtures.
Use unit prices and standard sizes to project totals, avoiding guesswork. Capture installed depths, load ratings, and delivery timelines to align with your schedule. Focus on data-driven choices: drawer depths, hinge types, and finish durability that affect lifecycle costs.
Record warranty terms, service intervals, and replacement cycles for high-use items. Compare materials by maintenance requirements and impact on indoor air quality. Ensure compliance with local codes for fixed fixtures, fire safety, and accessibility where applicable, so procurement aligns with budget buffers and risk planning.
Utilities Installations
To pull from the prior fixtures and fittings data, you’ll scope out the interior utilities and their installations with a clear, data-driven lens.
You’ll map costs for electrical, plumbing, and climate components, focusing on scale, efficiency, and redundancy.
Start with the electrical panel, feeders, outlets, and lighting plans, then quantify wire gauge, conduit runs, and circuit counts.
For plumbing, estimate supply and waste lines, fixtures, and insulation, noting pressure, temperature, and leak risk.
HVAC decisions hinge on heat loss, insulation R-values, and system efficiency, translating specs into annual operating costs.
Include permits, inspection fees, and contingency lines to cover unplanned work.
Compile unit costs, labor rates, and build-time impact, presenting a transparent, defensible subtotal that aligns with the overall project budget.
Contingencies, Maintenance, and Hidden Fees
Contingencies, maintenance, and hidden fees can substantially influence the total garden room budget, so it’s essential to quantify them upfront. You should build a risk buffer, commonly 5–15% of hard costs, to cover design changes, permits, and delivery delays.
Track maintenance costs by topic: exterior coatings, roof reseal, plumbing checks, and electrical inspections, estimating annualized figures over the project life. Hidden fees often arise from permit surcharges, impact fees, or expedited service, so verify itemized bids and request transparent fee schedules.
Schedule maintenance cycles based on equipment lifespans and climate, budgeting for HVAC filters, drainage, and pest treatments. Document all contingencies in a living cost forecast, updating quarterly as prices shift.
Use historical data, supplier quotes, and warranty terms to refine accuracy and prevent overruns.
Conclusion
From the ledger to the latch, you’ll see the costs line up like neatly stacked bricks. Picture a blueprint turning into a sunlit room: foundations firm, framing square, insulation tight, and roofing sealed against rain. The fixtures glow with purpose, utilities humming like a quiet river. When you account for contingencies, the total reads clear and steady, a measured map from ground to glow. Your garden room isn’t whimsy—it’s a precisely priced shell summoning daylight and function.
